Main Components of FDM 3D Printers
11 Things to Consider When Choosing Your First or Next Desktop FDM 3D Printer
11 Things to Consider When Choosing Your First or Next Desktop FDM 3D Printer
By knowing the main components of FDM 3D printers, how they work, and what they are capable of we can:
Layer thickness is the minimum thickness of a layer that a printer can lay down in a single pass. The smaller the number – smoother and more detailed the print is, but the process will be slower. Most desktop FDM 3D printers work with layer thickness of 0.1mm to 0.3mm, but are able to create layers thinner than 100 microns (0.1mm). On the other hand SLA/DLP 3D Printers can print with a resolution down to 20 microns (0.020mm). And some manufacturers claim that they can achieve precision down to the nano spectrum of the meter. Lulzbot Taz 5/6 can achieve 0.065mm that equals 65 microns.
100 microns = 0.1mm = 0.00394inches
Build area is the maximum size of an object that you can create with the 3D printer. It’s measured in XYZ dimension. For example 8 inch wide (X) by 8 inch deep (Y) by 10 inch high – 8x8x10 inches. More complicated or bigger print jobs can be split into smaller parts than can be combined afterwards.
Most FDM 3D Printers work with 1.75mm or 3mm filament diameter. The trend is 1.75mm, but few of the most popular manufacturers stick with 3mm. Machines with Bolden Extruder setup work better using 1.75mm and 3D printers with Direct Drive mostly use 3mm. There are exceptions from that principle. Some people simply prefer one over the other. Or in case you own a few different brands of FDM 3D printers it’s more practical if you stick to only one kind of filament size.
The Hot End is one of the, if not, the most important part of the 3D printer. This is where the plastic is melted and extruded in a little tiny layers. There are many different types of Hot Ends available on the market today.

While the old hot ends (PEEK based) were able to print only with one or two materials, the new ones today can be used with variety of thermoplastics. PEEK based hot ends used to jam a lot if not maintained properly and the maximum temperature limit was about 230°C.
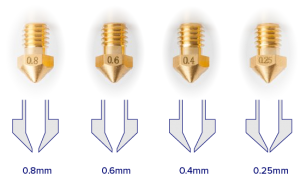
The Nozzle is the tip of the Hot End where the plastics comes out. It needs to be exchangeable when needed. The nozzle size is really important. It usually varies from 0.25mm to 0.75mm. The most common size is 0.5mm. The best practice is to change the nozzle sizes depending on your design and desired results.
The Extruder is the part that feeds the filament to the hot end. There are two different types of extruders available. It’s an outgoing conversation which one is better. Like most things some people prefer one over the other!
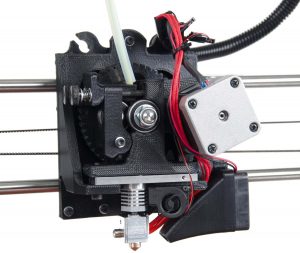 Direct
DirectWhen the filament is fed directly to the Hot End from the motor spindle. With this mechanism the Extruder is mounted on top of the hot end. It allows finer control over the extrusion and is easier to work with.
When the filament is fed form a certain distance to the Hot End (the extruder is physically separated from the hot end). The difference is that the filament has to travel a distance until it reaches the hot end through a tube. This type of mechanism reduces weight and allows for faster movement and less vibrations. In theory should produce more accurate prints in higher speed because there is less moment to overcome when changing direction. It’s harder to print certain filaments like Flexible. Due to the distance it’s oozing more, because the retraction is not as effective. Bowden extruders require better extrusion and retraction calibration
The cooling fan plays a really important role in the 3D printing process and it’s a must have feature. Not all 3D printing materials require active cooling, but it’s truly beneficial for most 3D prints. Some machines use only one fan, where others can have up to 3. The cooling fan will dramatically improve overhanging features, will crisp the sharp edges, and will result in good bridging capabilities.
Something important to understand here is that not all cooling fans are created equal. Some machines use a 25mm, others – 40mm. Some fans are designed to blow at the mid hot end area, some are focused at the tip of the nozzle and some have a different shaped ducts.
A heated bed is required for all high temperature extrusion filaments like ABS, HIPS, Polycarbonate, Nylon and it is very beneficial for almost all the materials. It will keep the plastic warm during the printing process and prevent it from warping. Also it will ensure a better adhesion between the layers, which will result in a better structural integrity of the printed parts. Heated Bed is crucial for the first layer to ensure a good level foundation. The temperature usually will be between 40°C to 110°C and it’s not a finger friendly zone!
Unheated beds can work only with PLA based plastics and TPUs , which has a lesser tendency to warp during cooling. Usually the bed is covered with PEI, PET or Painters blue tape to which the material adheres.

The LCD Display controller allows you to 3D print without the need of a computer connected or using a software host such as Cura. It needs a SD card to read the G-code instructions. The display allows more efficient space usage and frees up your computer for other tasks. It’s perfect for day-to-day printing and will be used in the majority of your print jobs.

With a multiple extruders you can print in multiple colors or materials simultaneously by assigning each extruder specific color or material. Some printers can be upgraded from single to multiple extruders, some can’t. The biggest benefit of multiple extruders is when you print you can set your support structures with a different material that can be dissolved in water or some other type of solvent, depending on the materials used!
Last updated: 4/28/2017
Hi
Actually I want to make my own 3d printer what parts will i need can you please help me
Hi there,
We can help you with the selection of some of the parts.
Do you know what type of a machine you’d like to build?
Use the contact form on the Website so we can get in touch with it.
Thank you!
Good Evening Sir! I’m Joel from Philippines. I also would like to have a help on selecting some parts on my 3D printer. It’s our Thesis Project, 3D printer using Chocolates.
here is my email, Joel.S.Santos10000119401@gmail.com
Thank you so much!
Hi Nencho,
We provided some components to local 3D printer customers, if you still need some help please contact me freely.
My email is k_sales01@163.com
Thiѕ articlе gives cleaг idea designed for the new սsers of Ьlogging, that genuinely how to do running
a blog.
Can someone actually create a printer out of 3D Printer?
Well, the answer is yes and no. You can partially use a printer for some of the components. Most definitely you will have to buy the electronics and some hardware. Some manufacturers claim that their machines are made out if 80% 3D printed parts.
Yes …..very soon I need in touch
Hi. We are looking for a 3D printing solution for concrete printing. Please suggest possible variations which could work out.
Hii we are designing a 3d printer for constructed houses and building bricks. What are the variation in that way.
Please tell us.
Hi
I want to make my own 3d printer what parts will i need can you suggest me??
Here you can find out the main components. In case you are not able to find then get in touch with us here.
Hiii, I want to know the function of every part in sequence.
It’s always been a dream of mine to buy a 3D printer, but I wanted to perform some research before I get one. I really like that you say to try and stick to one filament size when starting out. It would be nice to know that you won’t have to worry about changing out things if you get different colors of the same size.
Hello I would love to get in contact about how to make a 3D printer from scratch and what components I would need please email me at dominikboltnar@gmail.com